Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis. Between 80 and 90 percent of people with psoriasis have this type, which manifests as thickened, inflamed lesions called plaques. On lighter skin, plaques can appear pink or reddish. On skin of color, they may be thicker and look violet, grayish, or brown. The skin can have a silver, scaled texture, too. Plaques most often show up on the elbows, knees, back, and scalp, though they can appear on other areas of the body, as well. These symptoms are common enough that plaque psoriasis is sometimes simply referred to as psoriasis.
But there are other types of psoriasis, which have different symptoms. It is possible for a person to have more than one type of psoriasis at the same time and for psoriasis symptoms to change over time. Here, we look at the different types of psoriasis and what to do if you notice new skin symptoms.
Types of psoriasis and symptoms
In addition to plaque psoriasis, the other major forms of psoriasis are:
Inverse psoriasis. With inverse psoriasis, shiny, smooth lesions can appear purplish or dark brown on skin of color—or darker than the surrounding skin. On people with lighter skin, it appears red. These lesions affect areas of the body where skin folds against skin, such as the underarms, under the breasts, the groin, and the buttocks. While it can occur on its own, inverse psoriasis more commonly occurs when a person also has plaque psoriasis or other psoriasis symptoms on other areas of their body.
Guttate psoriasis. Guttate psoriasis is the second-most common type of psoriasis and is an example of how psoriasis symptoms can change over time—up to 40 percent of people who have guttate psoriasis develop plaque psoriasis. This type causes small lesions that are scaled and either round or drop-shaped. It is most common in children and people under the age of 30. It typically develops suddenly, often in response to an infection like strep throat.
Pustular psoriasis. Pustular psoriasis is another example of how psoriasis symptoms can change with time. This type cases small, white pustules, which can look like pimples. It is rare, but often severe, and can affect the hands and feet or other parts of the body. A flare of pustular psoriasis can precede plaque psoriasis symptoms, occur alongside plaque psoriasis symptoms, occur after a flare of plaque psoriasis, or occur on its own.
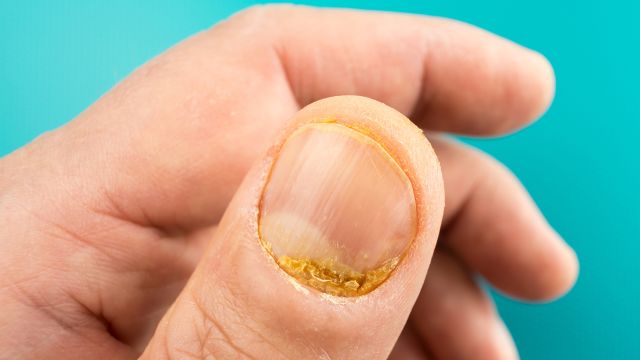
Nail psoriasis. Nail psoriasis is common among people who have psoriasis, and also among people that have psoriatic arthritis. It affects the nails of the fingers and toes, causing the nails to thicken, crumble, become pitted, and separate from the nail bed. Up to about 80 percent of people with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis experience these symptoms.
Erythrodermic psoriasis. Only about 3 percent of people with psoriasis experience erythrodermic psoriasis, a life-threatening form of the disease that causes inflammation across most of the body and the rapid loss of large areas of skin. Complications can be life-threatening. It usually occurs in people with severe and uncontrolled psoriasis, and often in response to a trigger, such as medication withdrawal, an allergic reaction to a medication, an infection, or an injury like sunburn.
Remember that psoriasis is unpredictable and these symptoms can vary from person to person.
Other skin conditions
It is also important to remember that a new symptom may not necessarily be psoriasis. There are many conditions that affect the skin—such as eczema, fungal infections, and seborrheic dermatitis—and having one does not exclude having another.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about all of your symptoms and any new symptoms you experience. Different types of psoriasis may require different approaches to treatment, and skin conditions that are not psoriasis will require different treatments.
As mentioned above, psoriasis varies from person to person and it is often unpredictable. Your best source of information about your health and your skin is your healthcare provider.